How To Heal An Avoidant Attachment Style Pdf Free Download – Step to heal Avoidant Attachment!
Introduction:
Understanding our attachment styles can significantly influence our relationships and personal well-being. Avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong inclination towards emotional distance, self-reliance, and an overwhelming fear of intimacy. Often rooted in early childhood experiences, individuals with this attachment style may have learned to minimize emotional closeness as a protective mechanism against perceived vulnerability.
The importance of healing from an avoidant attachment style cannot be overstated. Unhealed attachment patterns can lead to challenges in forming meaningful relationships, experiencing deep emotional connections, and achieving overall life satisfaction. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding and healing from avoidant attachment, with practical steps and resources to aid in the journey toward healthier relationships.
Section 1: Identifying Avoidant Attachment:
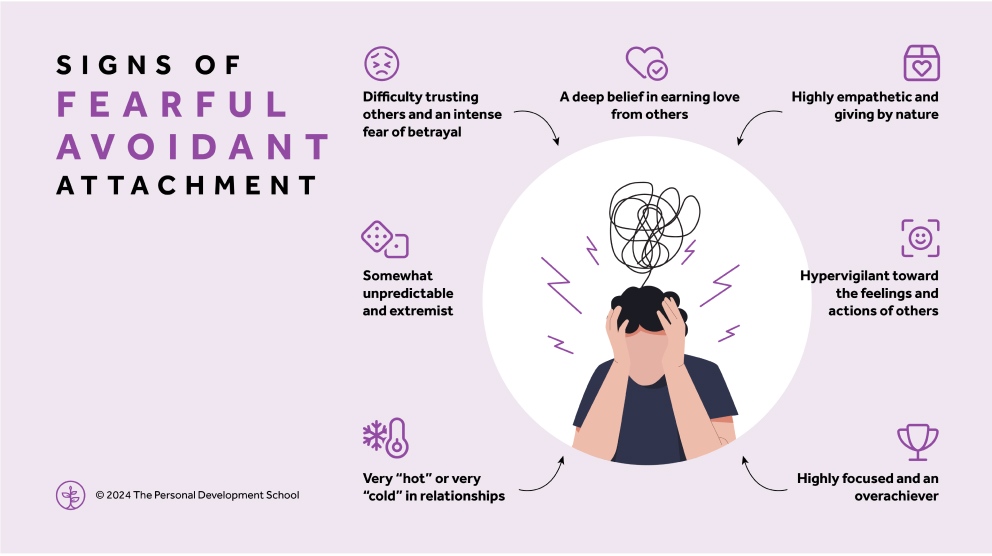
Signs and Symptoms:
Recognizing the signs of avoidant attachment is crucial for initiating the healing process. Common traits include:
- Emotional Detachment: A tendency to keep a safe emotional distance from others, often leading to superficial relationships.
- Fear of Intimacy: Difficulty trusting others and allowing oneself to be vulnerable, which can result in avoiding deep connections.
- Self-Reliance: A belief that one can only rely on oneself, leading to feelings of isolation.
- Dismissive Attitude: Often downplaying the importance of relationships and dismissing emotional needs as unnecessary or burdensome.
Self-Reflection Exercises:
Self-reflection is a powerful tool for identifying avoidant behaviors.Try reflecting on the following journaling prompts:
- Reflect on Past Relationships: What patterns do you notice in how you relate to others? Do you often pull away when things get too close?
- Emotional Inventory: List instances where you felt uncomfortable expressing your feelings. What fears were present?
- Identify Triggers: Think about situations that trigger your avoidance. How do you typically react?
Section 2: The Healing Process:
The first step toward healing is acknowledging your attachment style without judgment. This means understanding that your avoidance is a learned behavior, often developed to protect yourself from emotional pain. Cultivating self-awareness about these patterns can be transformative.
Therapeutic Approaches:
Various therapeutic methods can assist in healing:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This approach helps individuals recognize and challenge negative thought patterns surrounding intimacy and relationships. For instance, a person might learn to replace thoughts like “I don’t need anyone” with “It’s okay to need support.”
- Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT): EFT emphasizes understanding emotional responses and how they affect relationships. By focusing on feelings, individuals can learn to express their needs more openly and recognize the importance of emotional connection.
- Mindfulness and Self-Compassion: Incorporating mindfulness practices can help individuals stay present and become aware of their emotional states. Self-compassion exercises encourage kindness toward oneself, which can mitigate the fear of vulnerability.
Section 3: Building Secure Attachments:

Developing Emotional Intimacy:
Building emotional intimacy is essential for overcoming avoidant tendencies. Start small by sharing personal stories with trusted friends or partners. Gradually increase the depth of your conversations, allowing yourself to express your thoughts and feelings without the fear of judgment.
Effective Communication:
Clear communication is a cornerstone of healthy relationships. Practice expressing your feelings and needs using “I” statements (e.g., “I feel anxious when we don’t communicate frequently”). This approach reduces defensiveness and fosters understanding.
Establishing Trust:
Trust is vital in building secure attachments. Focus on being reliable and consistent in your actions. Small acts of kindness and support can help create a sense of safety in relationships, making it easier to open up emotionally.
Section 4: Practical Exercises:
Gradual Exposure:
Engaging in gradual exposure can help desensitize feelings of anxiety around intimacy. Start with minor acts of vulnerability, such as sharing a small personal detail or asking for help with something minor. Over time, increase the intensity of these exchanges.
Role-Playing:
Role-playing exercises can be beneficial for practicing communication skills. Work with a trusted friend or therapist to simulate conversations where you express feelings or needs. This can help you gain confidence in real-life situations.
Creating Safe Spaces:
Establish environments where emotional expression is welcomed. This could be through designated “check-in” times with loved ones, where everyone shares their feelings openly in a non-judgmental space.
FAQ’s
1. What is avoidant attachment?
Avoidant attachment is an emotional style characterized by a fear of intimacy, emotional distance, and a preference for self-reliance, leading to superficial relationships.
2. What are the common signs of avoidant attachment?
Signs include emotional detachment, difficulty trusting others, a dismissive attitude toward relationships, and a tendency to avoid vulnerability.
3. How can I start healing from avoidant attachment?
Begin by acknowledging your attachment style, practicing self-reflection, and exploring therapeutic options like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT).
4. What role does self-reflection play in healing?
Self-reflection helps identify avoidant behaviors and triggers, allowing individuals to understand their patterns and work toward positive change.
5. Why is communication important in overcoming avoidant attachment?
Clear communication fosters understanding and connection, enabling individuals to express their feelings and needs, which is essential for building healthy relationships.
6. What therapeutic approaches can assist in healing?
Therapeutic methods such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT), and mindfulness practices are effective in addressing avoidant attachment.
7. How can I build emotional intimacy with others?
Start by sharing personal stories with trusted friends or partners, gradually increasing the depth of your conversations to foster trust and vulnerability.
8. What practical exercises can help with healing?
Gradual exposure to vulnerability, role-playing conversations, and creating safe spaces for emotional expression can support the healing process.
9. When should I consider seeking professional help?
If you find it challenging to manage relationships or feel overwhelmed by your avoidant tendencies, seeking help from a therapist can provide valuable support and guidance.
10. How long does it take to heal from avoidant attachment?
Healing is a personal journey that varies for each individual. With consistent effort and support, significant changes can be seen over months to years.
Conclusion
Healing from avoidant attachment requires self-awareness, patience, and intentional effort. By recognizing your patterns, practicing vulnerability, and using therapeutic approaches like CBT or EFT, you can gradually build deeper emotional connections. Though the journey takes time, it leads to more fulfilling relationships and a stronger sense of trust and intimacy.





