How Long Does It Take For Bulging Disk To Heal – Bulging Disc Recovery Time!
A bulging disc typically heals within 4 to 6 weeks with conservative treatments, though full recovery may take several months depending on the severity and individual factors.
In this article, we’ll explore how long it typically takes for a bulging disc to heal, what factors influence the healing process, and the best treatment strategies to speed up recovery.
What Is a Bulging Disc?
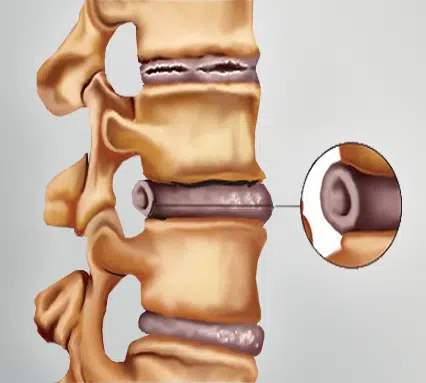
The spine is made up of vertebrae, and between each vertebra is a disc that acts as a cushion, absorbing shock and allowing movement. These discs are made of a tough outer layer and a soft inner layer. When a disc bulges, the soft inner material pushes out through the tougher outer layer but does not rupture entirely, causing pressure on nearby nerves.
In some cases, the bulge may cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area.
A bulging disc is not the same as a herniated disc, although the two terms are often used interchangeably.
A herniated disc occurs when the outer layer of the disc tears and the inner material leaks out, which can be more serious and painful. In contrast, a bulging disc is less severe, though it can still lead to significant discomfort.
How Long Does It Take for a Bulging Disc to Heal?
The healing time for a bulging disc can vary widely based on the extent of the disc’s bulge and the individual’s specific circumstances. On average, most people begin to feel better within 4 to 6 weeks with conservative treatments. However, it’s important to note that full recovery can take several months, and some people may continue to experience mild discomfort for a longer period.
Acute Recovery (4–6 weeks):
During the first few weeks of treatment, the focus is primarily on managing pain and inflammation, as well as preventing further damage to the disc. Most individuals can begin to see improvement during this phase, especially with rest, gentle movement, and physical therapy. By the end of this period, the disc may start to heal and reduce the pressure on the nerves.
Also Read: What Is The Fastest Way To Heal A Stress Fracture – Proven Tips!
Subacute Recovery (2–3 months):
After the initial phase, healing continues but at a slower pace. Individuals may still experience some discomfort, especially with certain movements or activities. However, by this point, the pain should be significantly reduced, and the individual can typically return to normal daily activities. If physical therapy is being followed, strengthening exercises and stretches will help improve mobility and support the spine.
Full Recovery (3–6 months or more):
Complete healing of a bulging disc may take several months, depending on the severity of the condition. During this time, strengthening and flexibility exercises become crucial to prevent future bulging or other spinal issues. While some people recover completely, others may experience occasional flare-ups or long-term discomfort.
Factors That Influence Healing Time:
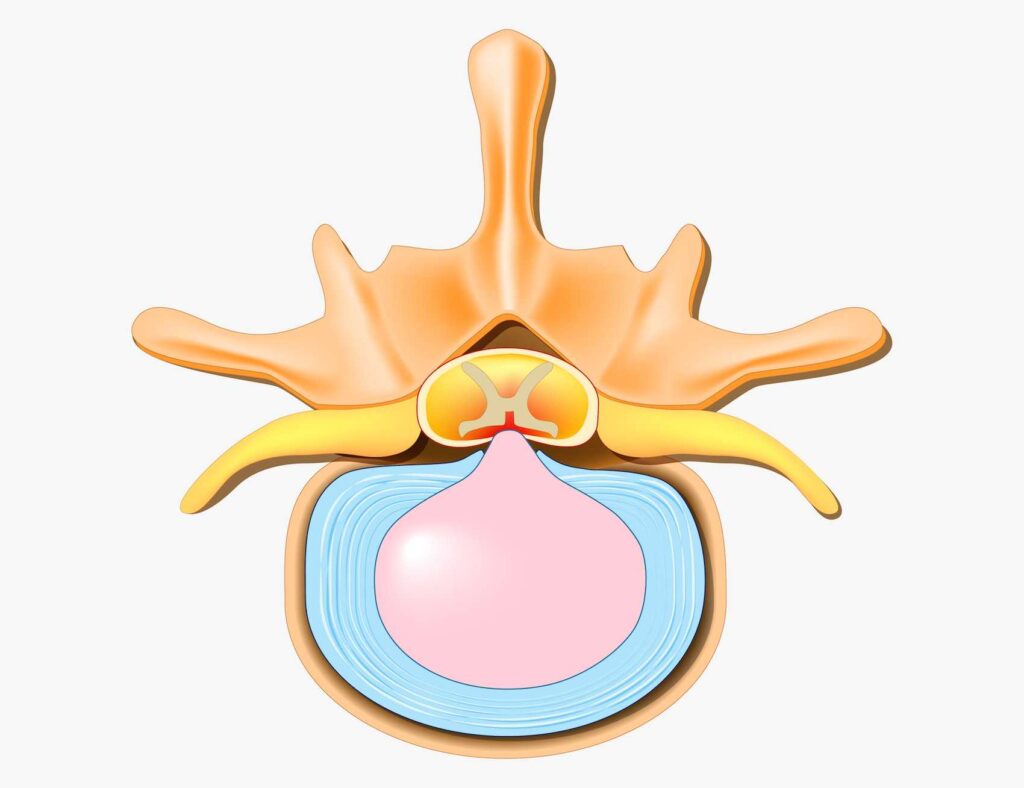
Several factors can impact how long it takes for a bulging disc to heal:
- Severity of the Bulge: A small bulge may heal faster than a large one. Larger bulges or those that put pressure on nearby nerves can cause more pain and may take longer to heal.
- Treatment Approach: Conservative treatments like physical therapy, chiropractic care, and medications can help speed up recovery, while invasive treatments such as injections or surgery may be necessary for more severe cases.
- Age and Overall Health: Younger individuals with fewer pre-existing health conditions typically heal faster. Older adults or those with conditions like obesity or poor posture may experience slower recovery times.
- Activity Level: Remaining active, yet avoiding activities that strain the spine, can promote healing. However, continuing strenuous activities that place pressure on the back may delay recovery.
Common Symptoms of a Bulging Disc:
The symptoms of a bulging disc can vary based on its location and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain is usually felt in the lower back, neck, or along the path of the nerve affected. It may radiate to the arms or legs.
- Numbness or Tingling: Nerve compression from a bulging disc can cause numbness or tingling sensations in the limbs.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the legs or arms may occur if the bulging disc presses on motor nerves.
- Limited Mobility: Pain and stiffness may make it difficult to move or bend in certain directions.
Treatment Options for a Bulging Disc:
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition. Most bulging discs heal with conservative treatment methods, while more severe cases may require additional interventions.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Rest is important during the acute phase to give the disc a chance to heal. Avoiding activities that aggravate the back, such as lifting heavy objects or engaging in intense physical exercise, is essential.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a central role in the recovery process. A physical therapist will teach specific exercises to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and promote healing. It also helps to reduce pressure on the affected disc and improves posture.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or muscle relaxants to ease discomfort.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area during the first 48 hours can help reduce swelling. Afterward, heat therapy (such as a heating pad) can be used to promote blood circulation and relieve muscle tightness.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments may help alleviate the pressure on the spine and improve alignment, but these should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider to avoid further injury.
- Injections: If conservative treatments fail, doctors may recommend spinal injections, such as corticosteroid injections, to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Surgery: In rare cases, when other treatments don’t provide relief, surgery may be necessary. Procedures like a discectomy (removing part of the disc) or spinal fusion may be recommended to relieve nerve compression and stabilize the spine.
Also Read: How To Heal A Pulled Back Muscle Overnight – Quick Relief Tips!
How to Speed Up Recovery?
While healing time can vary, there are steps you can take to accelerate the process:
- Maintain Proper Posture: Good posture helps to distribute the weight evenly across the spine and reduces strain on the affected disc.
- Stay Active with Caution: Engage in light activities like walking, swimming, or gentle stretching to increase circulation and support healing.
- Adhere to Your Treatment Plan: Consistently following the advice of your doctor, physical therapist, or chiropractor can help you heal faster.
- Strengthen Core Muscles: A strong core can reduce strain on the lower back and prevent future bulging discs
When to Seek Medical Help?
While most bulging discs improve with time and conservative treatment, certain signs may indicate the need for medical intervention:
- Persistent or severe pain that doesn’t improve with over-the-counter medications
- Numbness or tingling that worsens
- Weakness in the legs or arms that affects mobility
- Loss of bladder or bowel control, which could indicate nerve damage
If any of these symptoms occur, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to avoid complications.
FAQ’s
1. How long does it take for a bulging disc to heal?
A bulging disc typically heals in 4 to 6 weeks with conservative treatments, but full recovery can take several months.
2. What are the common symptoms of a bulging disc?
Symptoms include pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, and limited mobility depending on the location of the bulging disc.
3. Can physical therapy help with a bulging disc?
Yes, physical therapy is essential in the recovery process, helping to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pressure on the affected disc.
4. What factors affect the healing time of a bulging disc?
Factors include the severity of the bulge, treatment approach, age, overall health, and activity level.
5. When should I seek medical help for a bulging disc?
If you experience persistent pain, worsening numbness, weakness, or loss of bladder/bowel control, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Conclusion
A bulging disc generally heals within 4 to 6 weeks with proper care, though full recovery can take a few months. By adhering to a treatment plan that includes rest, physical therapy, and pain management, most people can recover without surgery. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider to explore other options and prevent long-term issues.