Can A Torn Achilles Tendon Heal On Its Own – Expert Insights!
A torn Achilles tendon can heal on its own if it’s a minor tear, but complete ruptures usually require surgery for full recovery.
This article delves into whether a torn Achilles tendon can heal on its own, various treatment methods, and recovery expectations. Read on to understand what approach suits different severities of the injury.
Understanding an Achilles Tendon Tear:
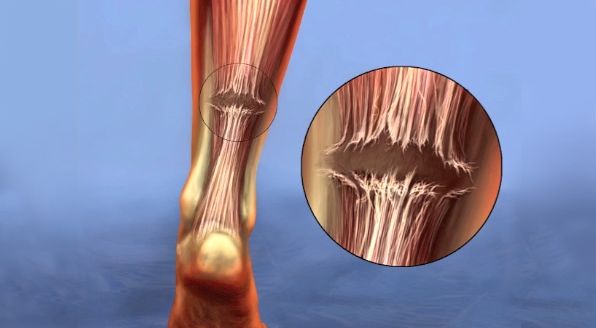
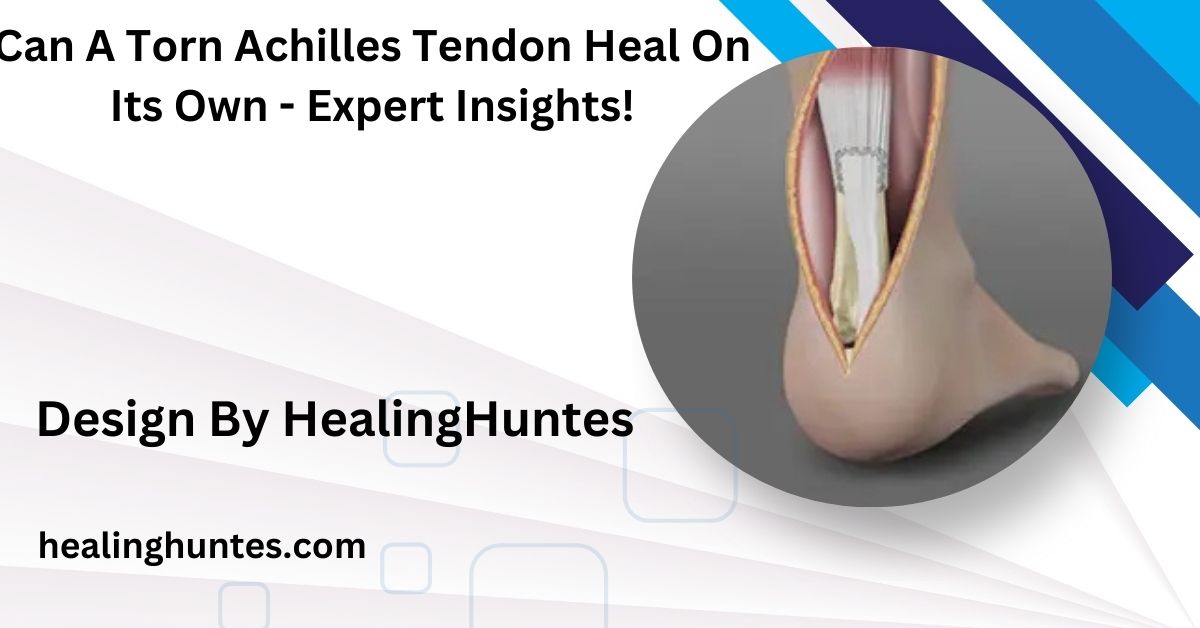
An Achilles tendon tear occurs when the tendon experiences excessive stress or strain, leading to a partial or complete rupture. Such injuries are prevalent among athletes or individuals engaging in physically demanding activities.
Causes of Achilles Tendon Tears:
Overuse and sudden physical strain are primary causes of a tear. Activities involving intense jumping, running, or abrupt changes in direction can overstress the tendon, especially without adequate preparation.
Symptoms of a Torn Achilles Tendon:
Signs of a tear include sudden, sharp pain at the back of the ankle, swelling, and difficulty walking. In severe cases, a popping sound at the time of injury often indicates a complete rupture.
Can the Achilles Tendon Heal Without Surgery:
The ability of an Achilles tendon to heal without surgery depends on the injury’s severity. Partial tears often respond well to non-surgical methods like rest and physical therapy. These approaches allow the tendon to regenerate naturally over time. However, complete ruptures generally require surgical repair, as they lack the stability needed for proper self-healing, potentially leading to complications without intervention.
Healing Potential for Partial Tears:
Partial tears have a better chance of healing without surgery. Non-surgical treatments help the tendon regenerate by keeping it immobilized and gradually restoring strength through physical therapy.
Also Read: How To Heal Wounds Faster – What Works and What Doesn’t!
Limitations in Natural Healing for Complete Tears:
Complete ruptures, however, typically require surgical intervention. Without proper treatment, a full tear can result in long-term weakness, limited functionality, and an increased likelihood of re-injury.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options:
Non-surgical treatments focus on allowing the tendon to heal while minimizing strain. Immobilization with a cast or brace keeps the foot in an optimal position for healing. Physical therapy gradually restores strength, flexibility, and mobility, aiding in recovery. Anti-inflammatory medications may also be used to manage pain and swelling. These treatments are effective for partial tears but require consistency and patience.
Immobilization for Healing:
Using a cast, boot, or brace helps keep the foot in a specific position, promoting natural healing. Immobilization ensures the torn fibers align and begin to repair over time.
Physical Therapy and Recovery:
Physical therapy is essential for restoring mobility and strength in the tendon. Therapists guide patients through exercises that gradually improve flexibility, balance, and functionality.
Surgical Treatment for a Torn Achilles Tendon:
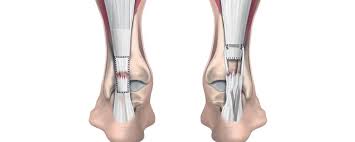
Surgery is often recommended for complete ruptures to restore full tendon functionality. The procedure involves stitching the torn ends together, ensuring a stronger and more stable recovery. Post-surgical care includes immobilization, followed by physical therapy to regain mobility. While surgery carries some risks, it significantly reduces the chance of re-injury and provides better long-term outcomes, especially for active individuals.
Procedure and Benefits:
During surgery, a surgeon makes an incision to locate and repair the torn tendon. This approach reduces the risk of re-rupture and improves long-term outcomes, especially for active individuals.
Post-Surgery Rehabilitation:
Recovery after surgery involves immobilization followed by physical therapy. While it speeds up the healing process compared to non-surgical methods, rehabilitation is still crucial for achieving full mobility.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations:
Recovery time varies depending on the treatment chosen and the injury’s severity. Non-surgical methods may take 6-12 months, requiring strict adherence to therapy. Surgical recovery is generally faster, with significant progress often seen in 4-6 months. Regardless of the method, patience is crucial as rushing the recovery process can lead to complications or reinjury. Proper follow-up care ensures the best results.
Non-Surgical Recovery Timeline:
Non-surgical recovery can take 6-12 months. This extended timeline is necessary to ensure the tendon heals properly and regains strength without re-injury.
Recovery After Surgery:
With surgery, most patients experience significant improvement within 4-6 months. However, physical therapy often continues beyond this period to restore optimal mobility.
Also Read: What Is The Fastest Way To Heal Intercostal Muscle Strain – A Step-by-Step Guide!
Factors Influencing Recovery:
Several factors affect recovery from an Achilles tendon injury. The severity of the tear plays a significant role, with partial tears healing faster than complete ruptures. Age and general health also influence recovery time, as younger and healthier individuals tend to heal more quickly. Additionally, the choice of treatment and adherence to rehabilitation plans directly impact the recovery process.
Severity of the Tear:
Partial tears have a higher chance of healing naturally, while complete tears often require surgical repair. Accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the best approach.
Age and Activity Level:
Younger individuals and those with active lifestyles tend to recover faster. Older adults may face challenges, such as reduced tendon elasticity, which can prolong healing.
Risks of Ignoring Treatment:
Neglecting treatment for a torn Achilles tendon can lead to chronic issues. Untreated injuries often result in persistent pain, reduced mobility, and long-term weakness in the affected leg. Over time, the risk of re-injury increases, as the tendon remains structurally compromised. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are essential to avoid complications and ensure a successful recovery, enabling a return to normal activities.
Chronic Pain and Reduced Mobility:
Untreated tears often result in persistent discomfort and limited range of motion. Over time, this can severely impact daily activities and quality of life.
Increased Risk of Re-Injury:
Failure to address a torn tendon can weaken the area, making it prone to further injury. Seeking timely treatment prevents such complications and ensures better outcomes.
FAQ’s
1. Can a torn Achilles tendon heal without medical intervention?
Partial tears may heal with rest and therapy, but complete ruptures need medical attention to restore functionality.
2. How long does it take for an Achilles tendon to heal?
Recovery varies, with non-surgical methods taking 6-12 months and surgical recovery averaging 4-6 months.
3. Can physical therapy fully restore a torn Achilles tendon?
Yes, physical therapy plays a key role in recovery, strengthening the tendon and improving flexibility after treatment.
4. What are the signs of a healed Achilles tendon?
Reduced pain, normal range of motion, and improved strength indicate healing. Regular check-ups confirm the recovery process.
5. Is surgery the best option for an Achilles tendon rupture?
Surgery is often the preferred choice for complete tears due to better long-term outcomes, especially for active individuals.
Conclusion
A torn Achilles tendon can sometimes heal on its own if the injury is minor, but complete tears typically require medical intervention for full recovery. Understanding the severity, exploring treatment options, and committing to rehabilitation are vital for a successful outcome. Whether opting for non-surgical methods or surgery, timely action ensures the best chances of regaining mobility and strength while avoiding long-term complications. Prioritize proper care for optimal recovery.