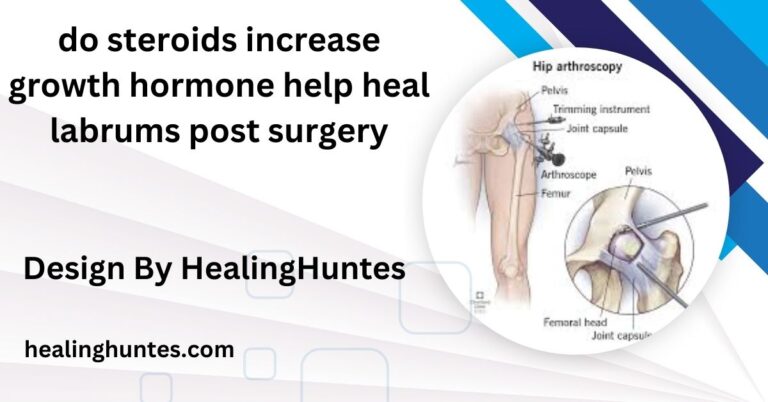
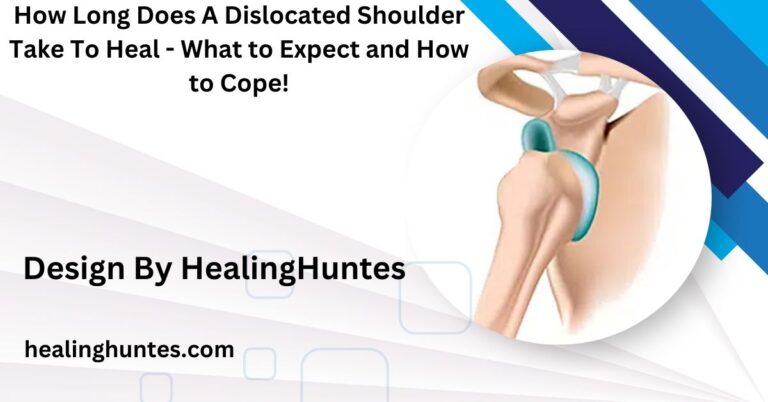
How Long Does A Torn Ligament Take To Heal – Torn Ligament Recovery Timeline!
Healing from a torn ligament can take weeks to months, depending on the severity. Treatments like rest, physical therapy, and surgery for severe cases aid recovery.
this article, we’ll explore typical recovery timelines, treatment options, and practical tips to support your healing journey for a safe and successful return to activity.
Understanding Ligament Injuries:
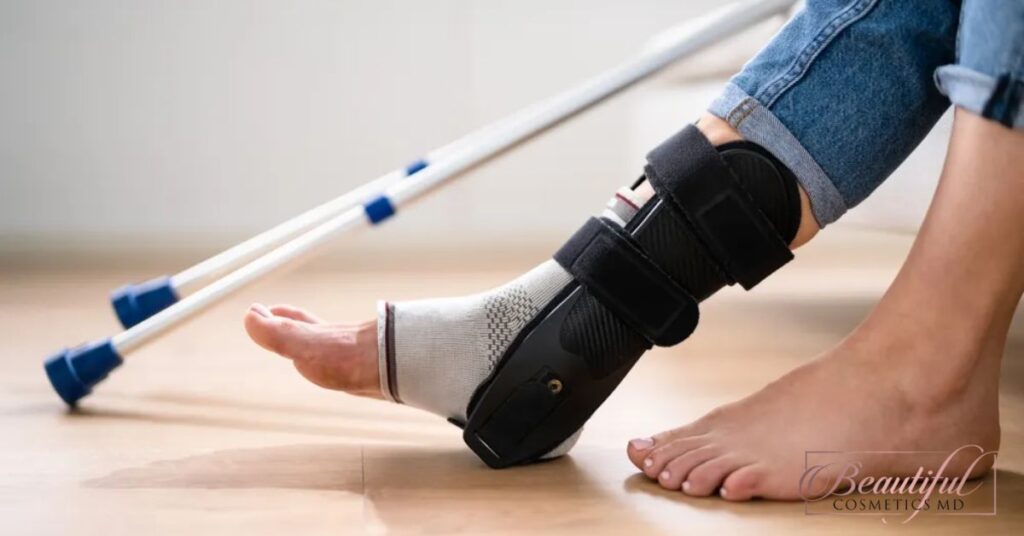
- Role of Ligaments in Joint Stability: Provide an overview of ligament structure, explaining how they connect bones to one another and offer joint stability. Use analogies, like comparing ligaments to ropes or bands that secure bones together, to help readers visualize.
- Types of Ligament Tears: Break down ligament tears by grades:
- Grade 1: Mild overstretching without a full tear. Minimal swelling, minor pain, and typically doesn’t affect joint stability.
- Grade 2: Partial tear causing significant pain, swelling, and mild to moderate joint instability.
- Grade 3: Complete tear leading to severe pain, considerable swelling, bruising, and substantial joint instability. Often, surgery is necessary.
Factors Affecting Ligament Healing Time:
- Age and Health: Older adults often face longer healing times due to reduced blood flow and cellular repair capabilities. Discuss how conditions like diabetes or arthritis can delay healing
- Activity Level and Lifestyle: Active individuals, especially athletes, may experience more severe tears due to the intensity of their movements. Conversely, sedentary lifestyles can prolong healing because muscles around the ligament might be weaker.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Adequate hydration and a nutrient-dense diet are crucial. Highlight how essential nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin A, and zinc support collagen synthesis and tissue repair
- Smoking and Alcohol Use: Both can inhibit healing by reducing oxygenation in tissues and interfering with cellular repair processes.
Average Healing Times for Common Ligament Tears:
- Ankle Ligaments: Generally take 4–12 weeks depending on severity.
- ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament): Often requires 6–12 months, especially with surgical repair.
- MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament): Averages 4–8 weeks for mild to moderate tears; complete tears can take several months, often without surgery.
- Shoulder and Elbow Ligaments: Recovery can range from 3 weeks to several months, based on the extent of injury and activity level.
Also Read: How To Heal From Childhood Trauma – Steps to Heal Trauma!
Treatment Approaches and Their Impact on Healing Time:
- Non-Surgical Interventions:
- Rest and Immobilization: Importance of rest during the initial phases to prevent further damage. Immobilization with a brace or cast can prevent strain on the ligament.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises for flexibility, range of motion, and strength in surrounding muscles to support the joint.
- Surgical Repair:
- When Surgery Is Recommended: Explain that Grade 3 ligament tears, especially in weight-bearing areas like the knee, may need surgical intervention.
- Post-Surgery Rehabilitation: Describe the 3–6 month recovery, which includes regaining range of motion, strength, and stability
Phases of Ligament Healing:
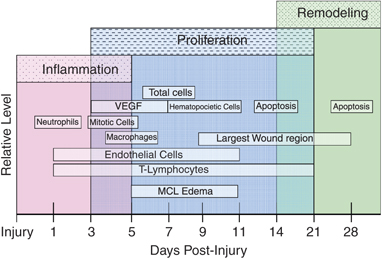
- Inflammatory Phase (1–2 Weeks): Pain, swelling, and redness characterize this phase as the body sends blood to start repair.
- Proliferative Phase (3–6 Weeks): New collagen fibers form as the body creates tissue to stabilize the ligament.
- Remodeling Phase (Up to 1 Year): The ligament strengthens and matures, but it may not regain full strength for several months.
Tips for Speeding Up Recovery:
- Diet and Supplements: Explain the role of anti-inflammatory foods (like leafy greens, berries, and nuts) in reducing swelling. Mention collagen supplements and vitamin C as crucial for collagen synthesis.
- Physical Therapy: Regular exercises under professional supervision can improve mobility and prevent muscle atrophy. Include an example of a basic exercise plan that incorporates gentle stretches, range-of-motion activities, and strengthening over time.
- Compression and Elevation: Benefits of reducing swelling and aiding lymphatic drainage to decrease pain and stiffness.
- Cryotherapy and Heat Therapy: Guidelines on when to use ice versus heat to manage pain and facilitate healing.
- Avoiding Re-Injury: Emphasize the importance of listening to the body’s signals and not pushing past discomfort or pain.
Mental and Emotional Aspects of Healing:
- Coping with Limited Mobility: Encourage setting realistic recovery goals and celebrating small improvements to stay motivated.
- Maintaining Positive Mindset: Explain how mental wellness practices, like mindfulness or visualization, can reduce stress and indirectly benefit healing.
- Dealing with Setbacks: Acknowledge that healing is not always linear and provide reassurance on what to expect during setbacks, emphasizing patience and self-compassion.
Also Read: How To Heal A Calf Strain Quickly – Is It Necessary!
Preventing Future Ligament Injuries:
- Strength Training for Joint Support: Offer exercises to strengthen muscles around major joints.
- Balance and Stability Exercises: Include ideas like single-leg stands and core workouts to improve stability and reduce injury risk.
- Proper Form and Technique: Stress the importance of form in sports or exercises, and recommend warm-ups with dynamic stretches before engaging in high-intensity activities.
With these expanded sections, the article becomes a thorough guide on ligament injuries, helping readers understand recovery timelines and how they can actively participate in their own healing journey. Would you like more specific examples or tips for physical therapy exercises.
FAQ’s
1. How long does it take to heal a torn ligament?
Healing time varies based on the severity of the tear. Mild injuries (Grade 1) may take 4–8 weeks, while more severe cases (Grade 3) can require 6–12 months for full recovery.
2. What are the different grades of ligament tears?
Ligament tears are classified into three grades: Grade 1 (mild overstretching), Grade 2 (partial tear with moderate symptoms), and Grade 3 (complete tear causing severe pain and instability). Each grade has distinct symptoms and recovery timelines.
3. What factors affect the healing time of a ligament tear?
Several factors can influence healing, including age, overall health, the severity of the tear, and lifestyle choices like diet and exercise. Active individuals or athletes may face longer recovery times due to more severe injuries.
4. When is surgical intervention necessary for ligament injuries?
Surgery is typically recommended for Grade 3 ligament tears or when joint stability is significantly compromised. Surgical options help restore function and stability, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knee.
5. How can I promote faster recovery from a ligament injury?
To speed up healing, prioritize rest, engage in physical therapy, and maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Avoiding re-injury and following rehabilitation guidelines are also crucial for a successful recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, healing from a torn ligament requires time, patience, and proper care. While recovery timelines vary, following recommended treatments and listening to your body can significantly aid the process. Focusing on physical therapy, maintaining a balanced diet, and gradually rebuilding strength are essential steps. With dedication to recovery, it’s possible to regain mobility and prevent future injuries, helping you return to your daily activities safely.