How Long Does A Torn Muscle Take To Heal – A Detailed Guide!
A torn muscle heals within 2-8 weeks for mild to moderate cases. Severe tears may take months, depending on treatment and rehabilitation.
This article provides a detailed guide on muscle healing, the factors affecting recovery, and tips to speed up the process.
Understanding a Torn Muscle:
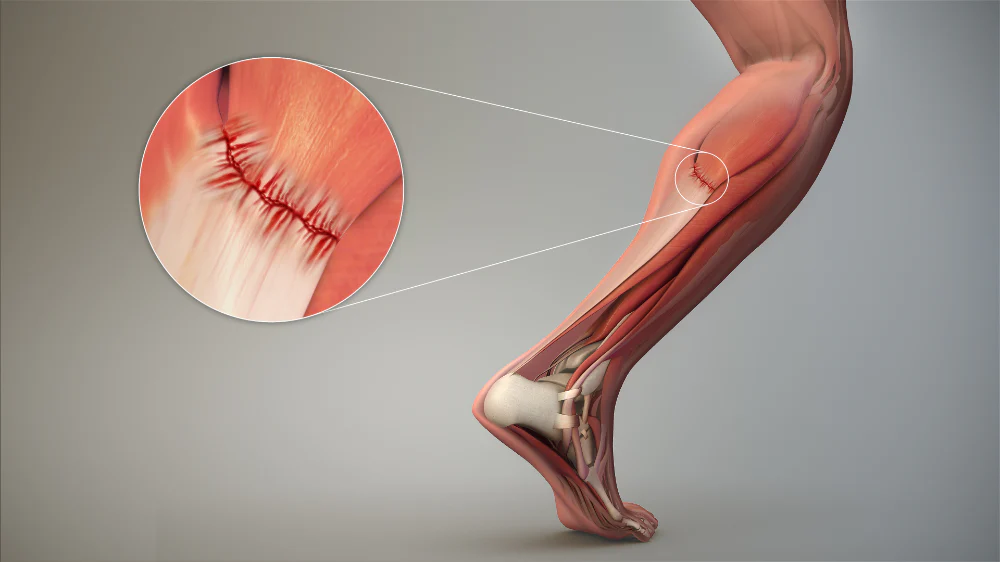
Muscle tears occur when muscle fibers stretch beyond their capacity or are subjected to sudden force. This injury is common in athletes but can affect anyone during physical activity or accidents. Symptoms of a torn muscle include sharp pain, swelling, bruising, and restricted movement. Severe tears may involve a complete rupture, requiring medical attention. Recognizing the signs early and seeking treatment is crucial for a smooth recovery.
Factors Affecting Muscle Healing Time:
A mild muscle tear heals within a few weeks, while moderate tears may require one to two months. Severe ruptures, however, often need surgery and extended recovery time. The severity of the tear directly impacts how long it will take to heal and the type of treatment needed.Tears in muscles that are used frequently, like those in the legs, take longer to heal due to the constant movement and strain.
Severity of the Tear:
Torn muscles are classified into three grades:
- Grade 1 (Mild): Minor damage to muscle fibers, heals within 2-3 weeks.
- Grade 2 (Moderate): Partial tearing of fibers, recovery takes 4-8 weeks.
- Grade 3 (Severe): Complete rupture, may require surgery and months of recovery.
Location of the Tear:
Muscles under constant strain, like those in the legs, take longer to heal due to regular movement. In contrast, less active muscles, like those in the arms, recover relatively faster.
Age and Overall Health:
Younger individuals heal faster due to better cell regeneration. Chronic conditions, like diabetes or poor circulation, can delay recovery. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle supports quicker healing.
Also Read: How Long Does It Take A Bone Bruise To Heal – Bone Bruise Healing Time!
Healing Stages of a Torn Muscle:
The repair phase follows, where the body works to regenerate muscle fibers using scar tissue. While movement improves during this phase, the muscle remains weak and needs to be treated with care. Gradual physical therapy exercises are introduced to help regain movement and strength.During the remodeling phase, scar tissue begins to align with muscle fibers, allowing the muscle to regain strength.
Stage 1: Acute Phase (First 48-72 Hours)
The initial stage involves inflammation as the body works to repair damaged fibers. Pain, swelling, and stiffness are common during this phase. Rest, ice application, and elevation are critical to reduce swelling and prevent further injury.
Stage 2: Repair Phase (3 Days to 6 Weeks)
In this stage, the body begins repairing torn fibers with scar tissue. Movement may improve, but the muscle is still weak. Physical therapy exercises are introduced gradually to rebuild strength and flexibility.
Stage 3: Remodeling Phase (6 Weeks to Several Months)
Scar tissue aligns with muscle fibers, restoring strength and function. This stage requires consistent rehabilitation and strengthening exercises to prevent re-injury and regain full mobility.
How to Speed Up Recovery:
Proper care and consistent effort can significantly reduce healing time. Here’s what to focus on:
- Rest and Protect the Muscle: Avoid activities that strain the injured area. Using supportive gear like braces or wraps can stabilize the muscle and aid recovery.
- Follow a Treatment Plan: Adhere to your doctor or physiotherapist’s guidance. Early physical therapy helps restore function while preventing stiffness or muscle atrophy.
- Focus on Nutrition: Eat a diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to support tissue repair. Nutrients like vitamin C and zinc are particularly beneficial for healing.
- Hydrate Adequately: Proper hydration improves circulation and accelerates the delivery of nutrients to the injured muscle.
- Gradual Reintroduction of Activities: As healing progresses, resume activities slowly and avoid pushing beyond limits. Rushing recovery can result in setbacks or further damage.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
Some torn muscles require professional care to prevent complications. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Visible deformities in the muscle.
- Inability to move the affected area.
Ignoring symptoms can prolong healing and lead to chronic conditions. Early intervention ensures better outcomes and minimizes long-term effects.
Complications of Untreated Muscle Tears:
Failure to address muscle tears can result in prolonged recovery and potential complications such as:
- Chronic pain or stiffness.
- Loss of muscle strength and flexibility.
- Development of scar tissue, restricting movement.
Taking prompt action and following a structured recovery plan can help avoid these issues.
FAQ’s
1. How long does a mild muscle tear take to heal?
A mild muscle tear typically heals within 2-3 weeks with rest and proper care.
2. Can I exercise while recovering from a torn muscle?
Light, supervised exercises may be introduced during recovery, but avoid strenuous activities that could worsen the injury.
3. Should I use heat or ice for a torn muscle?
Ice is recommended during the initial phase to reduce swelling. Heat can be used after a few days to relax muscles and improve blood flow.
4. Is surgery necessary for all torn muscles?
Surgery is only required for severe tears, such as complete ruptures. Most injuries heal with non-surgical treatments.
5. Can a torn muscle heal without treatment?
Minor tears may heal naturally, but untreated injuries risk improper healing, resulting in chronic pain or loss of function.
Conclusion
Healing a torn muscle varies based on the injury’s severity and treatment approach. With rest, proper care, and rehabilitation, recovery typically takes weeks to months. Rushing the process can lead to setbacks, so patience is crucial. Follow medical advice, focus on gradual strengthening, and prioritize rest for full recovery and restore functionality.