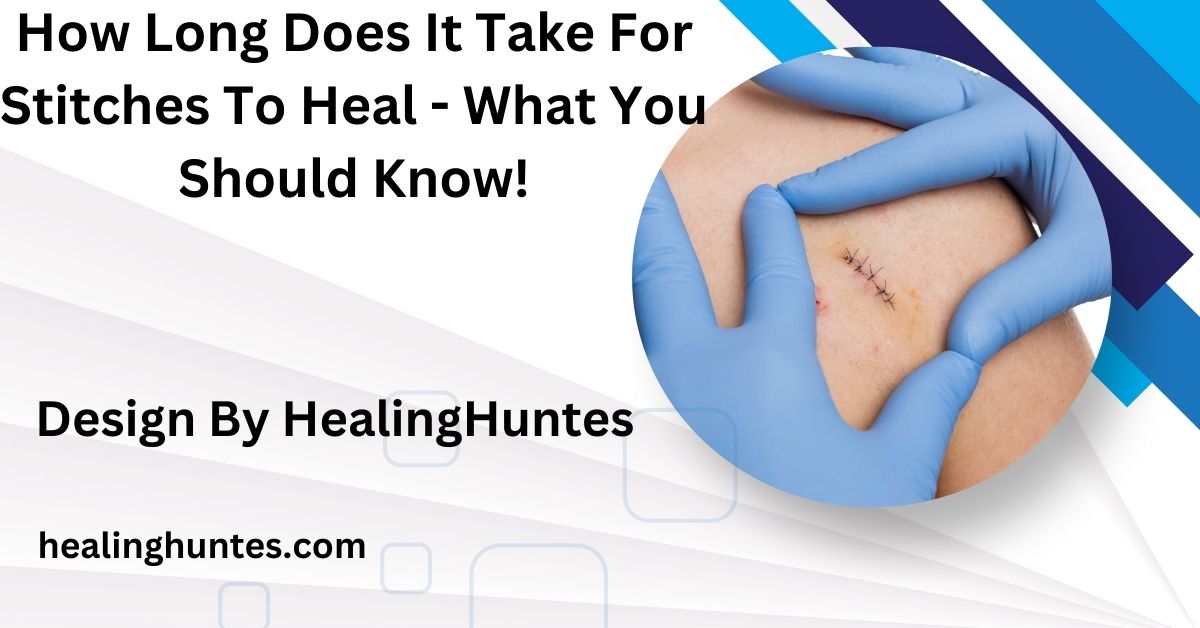
How Long Does It Take For Stitches To Heal – What You Should Know!
Stitches generally heal in 7 to 14 days, but proper care and individual health factors can influence recovery time.
This comprehensive guide explores the average healing timeline, factors that affect recovery, and tips to promote healing. It also highlights common complications and how to address them effectively.
Typical Healing Time for Stitches:
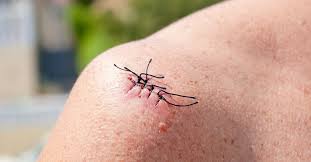
The time required for stitches to heal depends on several factors, including the type of wound, its location, and the individual’s overall health.
- Superficial wounds: These involve the skin’s surface and usually heal within 5 to 10 days. Stitches for such wounds are often removed after a week.
- Deeper wounds: Wounds involving multiple layers of tissue may take 2 to 3 weeks or longer to heal completely.
- Surgical incisions: Healing from surgeries often takes 10 to 14 days for external recovery, but deeper layers might take months.
Facial wounds typically heal faster due to better blood flow, while areas like joints or feet may take longer because of movement and stress.
Factors That Influence Stitches’ Healing Time:
Several factors affect how quickly stitches heal, including the size and location of the wound, your overall health, and adherence to proper wound care. Age, nutrition, and pre-existing conditions like diabetes or poor circulation also play significant roles. Understanding these factors can help improve healing outcomes.
Type and Severity of the Wound:
Clean, surgical cuts generally heal faster than jagged or contaminated wounds. The severity of the injury directly affects the healing duration; more tissue damage typically means longer recovery.
Also Read: Alternative Healing Endometriosis – Holistic Relief for Chronic Pain!
Location of the Wound:
Certain body parts heal quicker than others. For instance:
- Face and scalp: Tend to heal within a week due to high blood circulation.
- Hands, knees, and feet: May take longer due to frequent movement and exposure to external elements.
Individual Health and Age:
Younger individuals with strong immune systems tend to recover from wounds more quickly due to efficient cell regeneration. In contrast, conditions like diabetes, poor circulation, and advanced age can significantly slow down the healing process. These factors reduce blood flow to the affected area and hinder tissue repair.
Wound Care Practices:
Following proper wound care protocols, including regular cleaning and dressing, is crucial for timely healing. Neglecting these steps or failing to maintain hygiene can increase the risk of infection, which may delay recovery. Infections can also cause inflammation and tissue damage, further complicating the healing process.
Caring for Stitches to Promote Faster Healing:
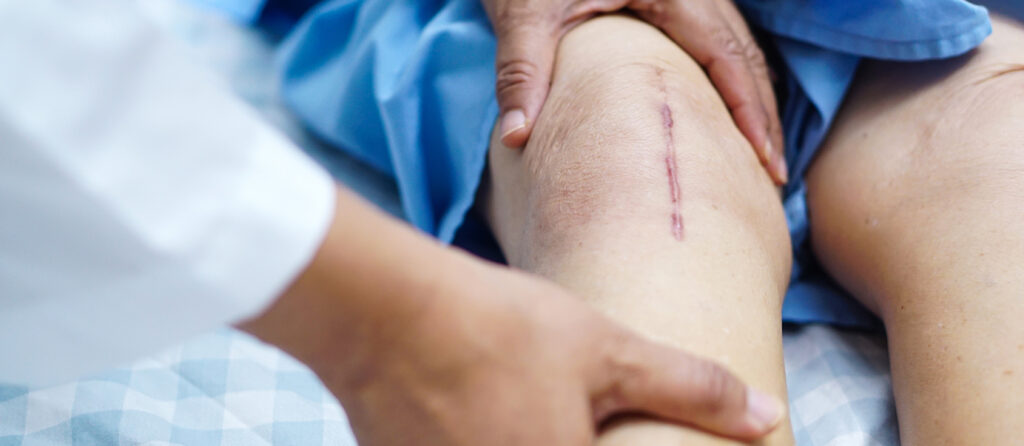
Proper care is crucial for speeding up the healing process. Keep the wound clean and dry, follow your doctor’s instructions for dressing changes, and avoid excessive movement around the stitched area. These steps help prevent infections and reduce the risk of complications, ensuring quicker recovery.
Keep the Wound Clean and Dry:
Maintaining wound cleanliness is essential to prevent infections. Use antiseptic solutions as prescribed by your doctor, and keep the wound dry, avoiding baths or soaking until the stitches are removed or fully healed.
Avoid Excessive Movement:
Wounds near joints or high-movement areas require special care. Limit unnecessary strain on these areas, and consider using a brace or bandage for additional support to aid in proper healing.
Maintain a Healthy Diet:
A nutrient-rich diet promotes faster healing. Focus on foods high in protein, vitamins A and C, and zinc, as these support tissue repair. Staying hydrated is equally crucial for the overall recovery process.
Follow Medical Instructions:
Adhering to your doctor’s wound care guidelines is vital for timely healing. Attend follow-up appointments as recommended, as skipping these could result in delayed recovery or undetected complications.
Also Read: When Is A Cold Sore Healed Enough To Kiss – A Guide to Safe Recovery!
Signs of Healing and Stitches Removal:
As your stitches heal, the wound should show signs of reduced redness, swelling, and no discharge. When the wound has closed and the skin feels firm, it’s time for stitch removal, typically within 7-14 days. Always follow your doctor’s advice for the right timing and care.
Normal Signs of Healing:
As your stitches heal, you may notice:
- Gradual reduction in redness and swelling.
- Formation of a protective scab over the wound.
- Mild itching, which is a sign of skin regeneration.
These are normal indicators that your body is repairing itself.
When to Remove Stitches:
Non-dissolvable stitches are generally removed within 7 to 14 days, depending on the wound type and location. For dissolvable stitches, the material breaks down naturally over 7 to 21 days. However, deeper surgical wounds may take longer.
Complications That May Delay Healing:
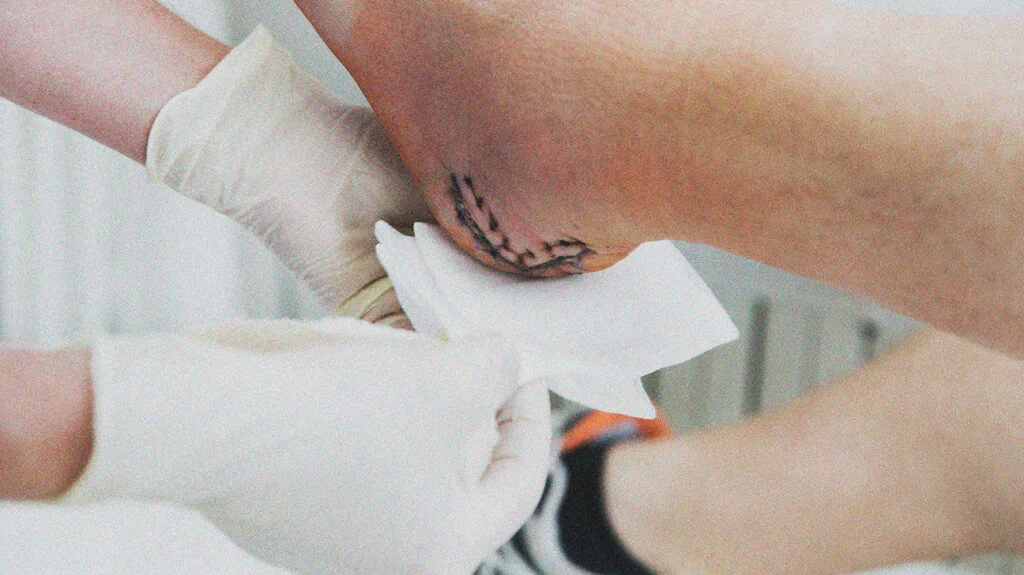
Infections, excessive movement of the wound, and poor nutrition can significantly delay the healing process. Other factors like underlying health conditions or smoking can also hinder recovery. It’s essential to address any complications early to prevent further delays.
Infection:
Infections are a significant risk for wounds with stitches. Symptoms include:
- Persistent redness, swelling, or warmth
- Discharge of pus or a foul smell
- Fever or chills accompanying wound discomfort
Seek medical attention immediately if these signs appear.
Smoking and Alcohol Use:
Smoking and alcohol consumption significantly impair the body’s healing abilities. Smoking reduces blood circulation to the wound, depriving it of essential oxygen, while excessive alcohol weakens the immune system, increasing the risk of infections and slowing recovery.
Poor Nutrition:
Inadequate nutrition can greatly delay wound healing. A diet lacking proteins, vitamins, and minerals essential for tissue repair can hinder recovery, emphasizing the need for nutrient-rich foods to support the healing process effectively.
Also Read: How To Heal From Rumination – Overcoming Rumination Fast!
Tips for Optimal Recovery:
Prepare for Stitches Removal:
Timely removal of stitches is crucial to prevent complications like embedded sutures or prolonged healing. Attend your scheduled appointment promptly, and consult your doctor if you notice redness or discomfort near the stitches before the removal date.
Protect Your Scar:
After stitches are removed, protecting the scar is vital for better healing and aesthetics. Apply sunscreen to prevent darkening and use scar-reducing creams as advised by your doctor. Proper post-care can significantly reduce the visibility of scars over time.
Be Mindful of Activity Levels:
Gradually return to physical activities after the wound has healed to avoid reopening it. For wounds in high-movement areas, follow your doctor’s advice on exercises and activity levels to ensure proper recovery without setbacks.
FAQ’s
1. How long does it take for stitches to heal?
Stitches usually heal in 7 to 14 days, but this can vary based on the wound’s location and depth.
2. Can dissolvable stitches take longer to heal?
No, the healing time for dissolvable stitches depends on the wound, but the stitches themselves dissolve naturally in about 7 to 21 days.
3. How can I tell if my stitches are infected?
Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, pus discharge, or fever. Consult a doctor if you notice these symptoms.
4. What can delay stitches healing?
Factors such as infection, poor nutrition, smoking, and underlying health conditions can slow down the healing process.
5. Can I shower with stitches?
Yes, but you may need to protect the wound with a waterproof dressing unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Conclusion
The healing time for stitches varies based on factors like wound type, location, and overall health. Proper care practices, such as keeping the wound clean, avoiding strain, and maintaining a nutrient-rich diet, can significantly enhance recovery. Attending follow-up appointments and addressing complications early are crucial for preventing delays in healing. Additionally, protecting the area and gradually resuming activities helps minimize scarring and ensures complete recovery.