How To Treat Wounds That Won’t Heal – Best Practices Explained!
To treat wounds that won’t heal, ensure proper wound care, maintain moisture, manage underlying health conditions, and consider specialized treatments while monitoring for infection signs.
In this guide, we’ll cover actionable steps to treat stubborn wounds, common treatment methods, and best practices to promote natural healing.
Understanding Why Some Wounds Won’t Heal:
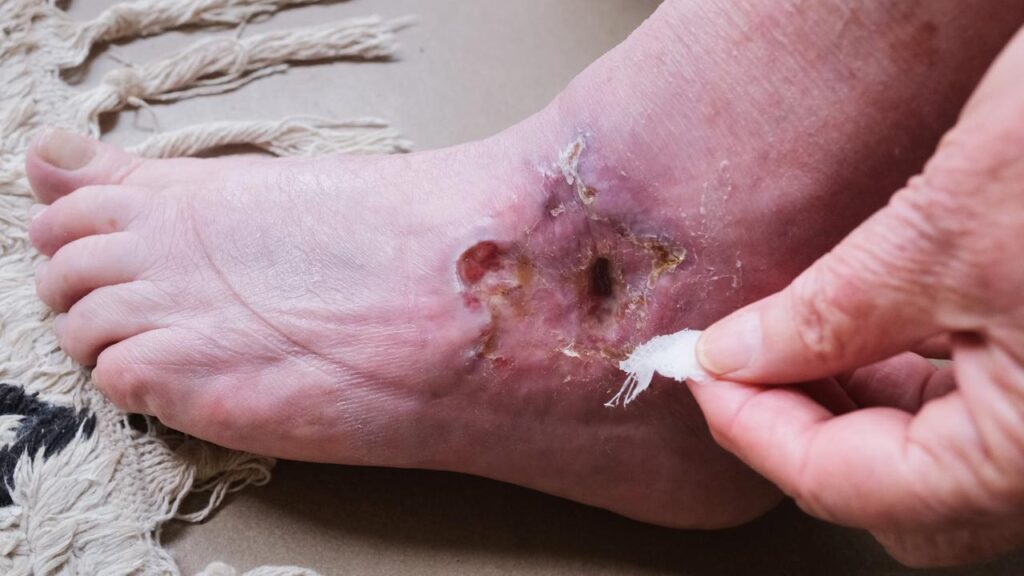
Most wounds heal within days or weeks, but sometimes they can persist, becoming chronic. Reasons for non-healing wounds include diabetes, poor circulation, immune system issues, or infections. Identifying the reason behind the prolonged healing process is the first step in effective treatment.
Step 1: Clean the Wound Properly
A clean wound is essential for healing. Start by washing your hands and gently cleaning the wound with mild soap and water. Avoid using alcohol or hydrogen peroxide, as these can irritate and damage healthy tissue.
Step 2: Maintain Proper Wound Moisture
Moisture helps wounds heal faster, contrary to the belief that they should dry out. Apply a thin layer of a healing ointment, such as petroleum jelly, and cover it with a clean bandage. Moisture helps new skin cells grow, aiding in faster and smoother healing.
Also Read: Full Teeth Extraction How Long To Heal – Tips And Timeline!
Step 3: Apply an Antibacterial Ointment
Using an over-the-counter antibacterial ointment can prevent infections that slow down healing. Apply a small amount to the wound after cleaning, but be cautious not to overuse it. Excessive antibiotic use can lead to resistant bacteria.
Step 4: Change Bandages Regularly
Changing the dressing daily, or as recommended by a healthcare provider, is crucial. Each time you change the bandage, clean the wound to prevent bacterial growth and allow fresh air to reach the tissue.
When to Seek Medical Help:
It’s crucial to seek medical help if a wound shows signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge. Additionally, if a wound fails to heal within two weeks or worsens despite home treatment, professional evaluation is necessary. Persistent pain or changes in sensation around the wound may also indicate complications that require medical intervention.
Home Remedies for Wounds That Won’t Heal:
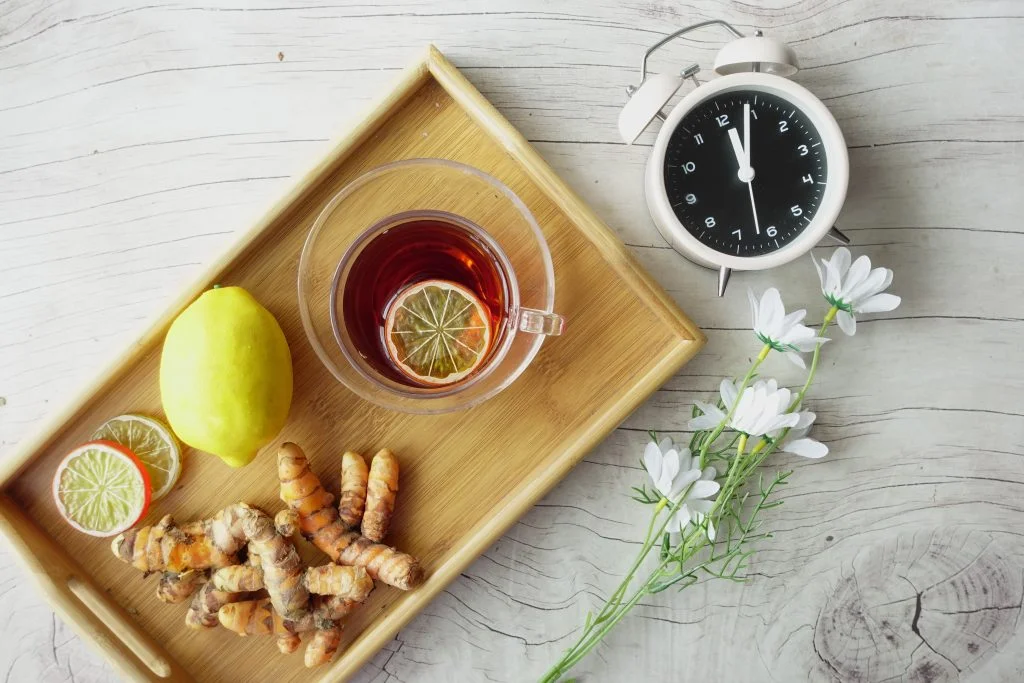

Honey:
Honey has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help cleanse wounds and prevent infections. Applying medical-grade honey creates a moist environment conducive to healing, which accelerates tissue regeneration. It’s especially beneficial for chronic or slow-healing wounds under medical guidance.
Aloe Vera:
Aloe vera is rich in vitamins and enzymes that soothe and moisturize the skin, promoting faster healing in minor wounds and burns. Its gel-like consistency provides a protective layer over the wound, reducing infection risk. Regular application can support tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation.
Turmeric:
Turmeric, known for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, can be applied as a paste to promote wound healing. Curcumin, its active compound, helps reduce swelling and fights bacteria, creating a conducive environment for the wound to heal. However, it’s best used on minor wounds and with medical advice.
Foods That Promote Healing:
- Protein: Found in lean meats, nuts, and dairy, protein is essential for tissue repair.
- Vitamin C: Foods like oranges, strawberries, and peppers are rich in vitamin C, which boosts collagen formation.
- Zinc: Zinc-rich foods, such as beans and whole grains, play a crucial role in immune function and wound repair.
Also Read: Can Healing Fix Broken Bones Dnd – Healing Rules Explained!
Avoid Habits That Slow Healing:
Avoiding habits that hinder healing, like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, is crucial, as they can reduce blood flow and impair immune function. Poor nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle also slow wound repair by depriving the body of essential healing nutrients. Making healthy lifestyle choices can significantly boost the body’s natural recovery process.
Specialized Treatments for Chronic Wounds:
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
This therapy involves breathing in 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which increases oxygen levels in the blood and promotes healing in stubborn wounds. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine if this treatment is appropriate.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) uses a vacuum device to apply controlled suction to the wound area, helping remove excess fluids and stimulate blood flow. This technique supports faster healing by reducing swelling and promoting tissue growth. NPWT is especially useful for chronic, non-healing wounds.
Skin Grafts
Skin grafts involve transplanting healthy skin from one area of the body to cover and treat a non-healing wound. This procedure provides essential tissue, promotes healing, and protects against infection. It’s often used when wounds are large, deep, or resistant to other treatments.
Managing Underlying Conditions:
Managing underlying conditions like diabetes, vascular disease, and immune disorders is crucial for wound healing. Proper control of blood sugar, regular exercise, and prescribed medications can help improve circulation and immune function. By keeping these conditions stable, the body is better able to repair and heal wounds effectively.
Also Read: How Long Does It Take For A Piercing To Heal – A Must-Read Guide!
Preventing Wounds That Won’t Heal:
Preventing wounds that resist healing involves proper skin care, maintaining good nutrition, and managing underlying health conditions like diabetes or poor circulation. Keeping the skin clean and moisturized reduces the risk of wounds, while a balanced diet supports tissue repair. Addressing health issues proactively can greatly reduce the chances of developing chronic wounds.
Importance of Regular Wound Monitoring:
Regular wound monitoring is crucial for detecting early signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge, which can help prevent complications. By assessing the wound daily, you can track healing progress and adjust care routines as needed. Frequent monitoring allows for timely medical intervention if the wound shows signs of deterioration, promoting faster and more effective healing.
FAQ’s
1. How long should a wound take to heal?
Minor wounds typically heal within a week or two. If healing takes longer than 3-4 weeks, consider consulting a doctor.
2. What are common signs of infection in a wound?
Symptoms include redness, warmth, swelling, pus, and a bad odor.
3. Is it okay to use hydrogen peroxide for wound care?
No, hydrogen peroxide can damage tissue. Use mild soap and water instead.
4. How often should I change my wound dressing?
Change dressings daily or as recommended by a healthcare provider.
5. What if I have diabetes and a wound won’t heal?
Diabetes can delay healing. Keep blood sugar under control and consult a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Effectively treating wounds that resist healing involves a comprehensive approach, combining meticulous wound care, adequate nutrition, and often specialized treatments like hyperbaric oxygen therapy or skin grafts. Ensuring proper hygiene and monitoring the wound daily are essential steps in reducing infection risks and encouraging tissue repair. Seeking timely medical advice can help address underlying conditions and ensure that treatment is optimized for each individual case, significantly enhancing recovery prospects.