How Long For Herniated Disc To Heal – What to Expect and When!
A herniated disc happens when the inner gel of a spinal disc bulges out, pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain. Healing generally takes a few weeks to 3-6 months, depending on severity and treatment.
This article explores the healing process, recovery time, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments that can help you on your journey to recovery.
Understanding a Herniated Disc:
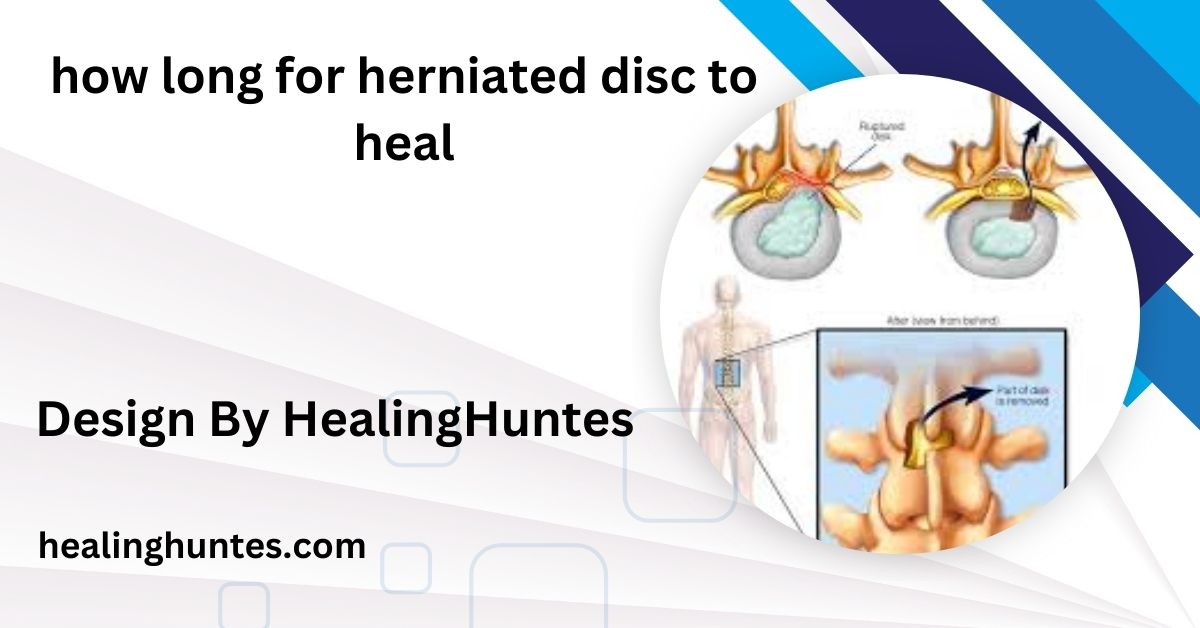
A herniated disc occurs when the soft gel-like center (nucleus) of a spinal disc bulges out through a tear in the tougher exterior (annulus). This can result in pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness, typically in the back, legs, or arms. Herniated discs often occur in the lumbar (lower back) or cervical (neck) regions of the spine.
Typical Signs of a Herniated Disc:
- Localized Pain: Pain can occur in the back or neck, depending on the location of the herniation.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that extends down the legs or arms, often described as sharp or shooting.
- Numbness or Tingling: A tingling sensation or numbness in the affected limbs.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the arms or legs, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks.
Elements That Impact Recovery Time:
The healing duration for a herniated disc varies based on several factors:
- Severity of Herniation: More severe herniations may require longer recovery times.
- Age: Older adults might experience a slower healing process due to decreased regenerative capacity.
- Overall Health: Pre-existing health conditions can impact recovery time.
- Treatment Approach: The effectiveness of the treatment plan plays a crucial role in recovery speed.
Also read: Can I Go To School While Healing From Car Accident – Returning to School After a Car Accident!
Typical Healing Timeline for a Herniated Disc:
Initial Recovery (Weeks 1-2):
In the first couple of weeks following a diagnosis, many individuals experience acute pain and discomfort. During this phase:
- Rest and Activity Modification: It is essential to avoid activities that worsen the pain. However, complete bed rest is generally not recommended, as it can lead to stiffness and delayed recovery.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may be used to manage pain and inflammation. Cold packs can help reduce swelling, while heat applications can soothe tight muscles.
Recovery Milestone (Weeks 3-6):
After the initial recovery period, many individuals begin to notice improvements in symptoms. This phase may involve:
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in a structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate nerve pressure. Therapists may utilize various techniques, including stretches, strengthening exercises, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
- Gradual Return to Activity: Low-impact activities, such as walking, swimming, or stationary cycling, may be gradually introduced as tolerated. This can help maintain cardiovascular fitness without placing undue strain on the back.
Long-Term Recovery (Weeks 6-12):
By the six to twelve-week mark, many individuals see significant improvements, although some may still experience lingering symptoms:
- Continued Physical Therapy: A tailored exercise program can assist in regaining strength and function. Exercises may focus on core stabilization and promoting proper body mechanics to prevent future injuries.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help assess progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Full Recovery (3-6 Months):
While many people begin to feel better within weeks, complete healing of the disc and surrounding tissues can take several months:
- Resumption of Activities: Most individuals can gradually return to their normal activities, including work and exercise, within three to six months. However, high-impact sports or activities that put excessive strain on the back should be approached with caution until fully healed.
- Ongoing Symptoms: Some patients may experience residual symptoms, which can often be managed through lifestyle changes, ongoing physical therapy, and home exercise programs.
Also read: What Do Fighters Use to Repair Healing – A Complete Guide!
Therapeutic Strategies for Herniated Discs:
Conservative Treatment Options:
- Medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications or prescription medications may be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A structured rehabilitation program can help restore strength, flexibility, and function.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal manipulation by a qualified chiropractor can help relieve pain and improve spinal alignment.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation around the affected nerve roots.
Surgical Treatments:
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief after several weeks or if significant neurological symptoms occur, surgical options may be considered:
- Discectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the herniated portion of the disc to relieve nerve pressure.
- Laminectomy: Removal of a small section of bone (the lamina) to create more space for the nerves.
- Spinal Fusion: In cases where stability is needed, surgeons may join two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Faster Recovery:
Making specific lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the healing process and prevent future injuries:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can add pressure to the spine, so maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential.
- Stay Active: Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling to improve overall fitness without straining the back.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting to reduce stress on the spine.
- Use Ergonomic Furniture: Invest in chairs and desks that promote good posture and provide proper lumbar support.
When to Seek Guidance from a Healthcare Provider:
While many cases of herniated discs improve with conservative treatment, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe Pain: Sudden, intense pain that does not improve with rest or medication.
- Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control: This could indicate a serious condition called cauda equina syndrome and requires immediate medical attention.
- Progressive Weakness or Numbness: If weakness or numbness in the arms or legs worsens, this could signify nerve damage that needs to be addressed promptly.
Also read: Do Steroids Increase Growth Hormone Help Heal Labrums Post Surgery – A Complete Guide!
FAQ’s
1. What is a herniated disc?
A herniated disc occurs when the inner gel of a spinal disc bulges out, potentially pressing on nearby nerves.
2. How long does it take for a herniated disc to heal?
Healing from a herniated disc typically takes a few weeks to 3-6 months, depending on the severity and treatment.
3. What treatments are available for a herniated disc?
Treatments include medications, physical therapy, chiropractic care, and possibly surgery if conservative options fail.
4. When should I seek medical attention for a herniated disc?
Seek medical help for severe pain, loss of bladder or bowel control, or worsening weakness and numbness.
5. What lifestyle changes can help in the recovery from a herniated disc?
Maintain a healthy weight, engage in low-impact exercises, practice good posture, and use ergonomic furniture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, healing from a herniated disc varies based on severity and treatment. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in low-impact exercises, practicing good posture, and using ergonomic furniture can support recovery. By following a tailored recovery plan that includes physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can enhance their chances of returning to normal activities and achieving a pain-free life.